Detecting malware using Yara integration
You can use the YARA integration with ThreatLockDown to scan files added or modified on an endpoint for malware. YARA is a tool to detect and classify malware artifacts.
In this use case, we demonstrate how to configure YARA with ThreatLockDown to detect malware on Linux and Windows endpoints.
To learn more about this integration with Wazuh, see the How to integrate ThreatLockDown with YARA section of the documentation.
Infrastructure
Endpoint |
Description |
|---|---|
Ubuntu 22.04 / RHEL 9.0 |
The YARA active response module scans new or modified files whenever the ThreatLockDown FIM module triggers an alert. |
Windows 11 |
The YARA active response module scans new or modified files whenever the ThreatLockDown FIM module triggers an alert. |
Configuration for Linux
Linux endpoint
Perform the following steps to install YARA, and configure the active response and FIM modules.
Download, compile and install YARA:
Ubuntu
$ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install -y make gcc autoconf libtool libssl-dev pkg-config jq $ sudo curl -LO https://github.com/VirusTotal/yara/archive/v4.2.3.tar.gz $ sudo tar -xvzf v4.2.3.tar.gz -C /usr/local/bin/ && rm -f v4.2.3.tar.gz $ cd /usr/local/bin/yara-4.2.3/ $ sudo ./bootstrap.sh && sudo ./configure && sudo make && sudo make install && sudo make check
RHEL
$ sudo yum makecache $ sudo yum install epel-release $ sudo yum update $ sudo yum install -y make automake gcc autoconf libtool openssl-devel pkg-config jq $ sudo curl -LO https://github.com/VirusTotal/yara/archive/v4.2.3.tar.gz $ sudo tar -xvzf v4.2.3.tar.gz -C /usr/local/bin/ && rm -f v4.2.3.tar.gz $ cd /usr/local/bin/yara-4.2.3/ $ sudo ./bootstrap.sh && sudo ./configure && sudo make && sudo make install && sudo make check
Test that YARA is running properly:
$ yarayara: wrong number of arguments Usage: yara [OPTION]... [NAMESPACE:]RULES_FILE... FILE | DIR | PID Try `--help` for more options
If the error message below is displayed:
/usr/local/bin/yara: error while loading shared libraries: libyara.so.9: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory.
This means that the loader doesn’t find the
libyaralibrary usually located in/usr/local/lib. Add the/usr/local/libpath to the/etc/ld.so.confloader configuration file to solve this:$ sudo su # echo "/usr/local/lib" >> /etc/ld.so.conf # ldconfig
Switch back to the previous user.
Download YARA detection rules:
$ sudo mkdir -p /tmp/yara/rules $ sudo curl 'https://valhalla.nextron-systems.com/api/v1/get' \ -H 'Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8' \ -H 'Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.5' \ --compressed \ -H 'Referer: https://valhalla.nextron-systems.com/' \ -H 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \ -H 'DNT: 1' -H 'Connection: keep-alive' -H 'Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1' \ --data 'demo=demo&apikey=1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111&format=text' \ -o /tmp/yara/rules/yara_rules.yar
Create a
yara.shscript in the/var/ossec/active-response/bin/directory. This is necessary for the Wazuh-YARA active response scans:#!/bin/bash # ThreatLockDown - Yara active response # Copyright (C) 2015-2022, ThreatLockDown Inc. # # This program is free software; you can redistribute it # and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public # License (version 2) as published by the FSF - Free Software # Foundation. #------------------------- Gather parameters -------------------------# # Extra arguments read INPUT_JSON YARA_PATH=$(echo $INPUT_JSON | jq -r .parameters.extra_args[1]) YARA_RULES=$(echo $INPUT_JSON | jq -r .parameters.extra_args[3]) FILENAME=$(echo $INPUT_JSON | jq -r .parameters.alert.syscheck.path) # Set LOG_FILE path LOG_FILE="logs/active-responses.log" size=0 actual_size=$(stat -c %s ${FILENAME}) while [ ${size} -ne ${actual_size} ]; do sleep 1 size=${actual_size} actual_size=$(stat -c %s ${FILENAME}) done #----------------------- Analyze parameters -----------------------# if [[ ! $YARA_PATH ]] || [[ ! $YARA_RULES ]] then echo "wazuh-yara: ERROR - Yara active response error. Yara path and rules parameters are mandatory." >> ${LOG_FILE} exit 1 fi #------------------------- Main workflow --------------------------# # Execute Yara scan on the specified filename yara_output="$("${YARA_PATH}"/yara -w -r "$YARA_RULES" "$FILENAME")" if [[ $yara_output != "" ]] then # Iterate every detected rule and append it to the LOG_FILE while read -r line; do echo "wazuh-yara: INFO - Scan result: $line" >> ${LOG_FILE} done <<< "$yara_output" fi exit 0;
Change
yara.shfile owner toroot:wazuhand file permissions to0750:$ sudo chown root:wazuh /var/ossec/active-response/bin/yara.sh $ sudo chmod 750 /var/ossec/active-response/bin/yara.sh
Add the following within the
<syscheck>block of the ThreatLockDown agent/var/ossec/etc/ossec.confconfiguration file to monitor the/tmp/yara/malwaredirectory:<directories realtime="yes">/tmp/yara/malware</directories>
Restart the ThreatLockDown agent to apply the configuration changes:
$ sudo systemctl restart wazuh-agent
ThreatLockDown server
Perform the following steps to configure ThreatLockDown to alert for file changes in the endpoint monitored directory. The steps also configure an active response script to trigger whenever a suspicious file is detected.
Add the following rules to the
/var/ossec/etc/rules/local_rules.xmlfile. The rules detect FIM events in the monitored directory. They also alert when the YARA integration finds malware. You can modify the rules to detect events from other directories:<group name="syscheck,"> <rule id="100300" level="7"> <if_sid>550</if_sid> <field name="file">/tmp/yara/malware/</field> <description>File modified in /tmp/yara/malware/ directory.</description> </rule> <rule id="100301" level="7"> <if_sid>554</if_sid> <field name="file">/tmp/yara/malware/</field> <description>File added to /tmp/yara/malware/ directory.</description> </rule> </group> <group name="yara,"> <rule id="108000" level="0"> <decoded_as>yara_decoder</decoded_as> <description>Yara grouping rule</description> </rule> <rule id="108001" level="12"> <if_sid>108000</if_sid> <match>wazuh-yara: INFO - Scan result: </match> <description>File "$(yara_scanned_file)" is a positive match. Yara rule: $(yara_rule)</description> </rule> </group>
Add the following decoders to the ThreatLockDown server
/var/ossec/etc/decoders/local_decoder.xmlfile. This allows extracting the information from YARA scan results:<decoder name="yara_decoder"> <prematch>wazuh-yara:</prematch> </decoder> <decoder name="yara_decoder1"> <parent>yara_decoder</parent> <regex>wazuh-yara: (\S+) - Scan result: (\S+) (\S+)</regex> <order>log_type, yara_rule, yara_scanned_file</order> </decoder>
Add the following configuration to the ThreatLockDown server
/var/ossec/etc/ossec.confconfiguration file. This configures the active response module to trigger after the rule 100300 and 100301 are fired:<ossec_config> <command> <name>yara_linux</name> <executable>yara.sh</executable> <extra_args>-yara_path /usr/local/bin -yara_rules /tmp/yara/rules/yara_rules.yar</extra_args> <timeout_allowed>no</timeout_allowed> </command> <active-response> <command>yara_linux</command> <location>local</location> <rules_id>100300,100301</rules_id> </active-response> </ossec_config>
Restart the ThreatLockDown manager to apply the configuration changes:
$ sudo systemctl restart wazuh-manager
Attack emulation
Create the script
/tmp/yara/malware/malware_downloader.shon the monitored endpoint to download malware samples:#!/bin/bash # ThreatLockDown - Malware Downloader for test purposes # Copyright (C) 2015-2022, ThreatLockDown Inc. # # This program is free software; you can redistribute it # and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public # License (version 2) as published by the FSF - Free Software # Foundation. function fetch_sample(){ curl -s -XGET "$1" -o "$2" } echo "WARNING: Downloading Malware samples, please use this script with caution." read -p " Do you want to continue? (y/n)" -n 1 -r ANSWER echo if [[ $ANSWER =~ ^[Yy]$ ]] then echo # Mirai echo "# Mirai: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mirai_(malware)" echo "Downloading malware sample..." fetch_sample "https://wazuh-demo.s3-us-west-1.amazonaws.com/mirai" "/tmp/yara/malware/mirai" && echo "Done!" || echo "Error while downloading." echo # Xbash echo "# Xbash: https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/unit42-xbash-combines-botnet-ransomware-coinmining-worm-targets-linux-windows/" echo "Downloading malware sample..." fetch_sample "https://wazuh-demo.s3-us-west-1.amazonaws.com/xbash" "/tmp/yara/malware/xbash" && echo "Done!" || echo "Error while downloading." echo # VPNFilter echo "# VPNFilter: https://news.sophos.com/en-us/2018/05/24/vpnfilter-botnet-a-sophoslabs-analysis/" echo "Downloading malware sample..." fetch_sample "https://wazuh-demo.s3-us-west-1.amazonaws.com/vpn_filter" "/tmp/yara/malware/vpn_filter" && echo "Done!" || echo "Error while downloading." echo # Webshell echo "# WebShell: https://github.com/SecWiki/WebShell-2/blob/master/Php/Worse%20Linux%20Shell.php" echo "Downloading malware sample..." fetch_sample "https://wazuh-demo.s3-us-west-1.amazonaws.com/webshell" "/tmp/yara/malware/webshell" && echo "Done!" || echo "Error while downloading." echo fi
Run the
malware_downloader.shscript to download malware samples to the/tmp/yara/malwaredirectory:$ sudo bash /tmp/yara/malware/malware_downloader.sh
Visualize the alerts
You can visualize the alert data in the ThreatLockDown dashboard. To do this, go to the Threat Hunting module and add the filters in the search bar to query the alerts.
rule.groups:yara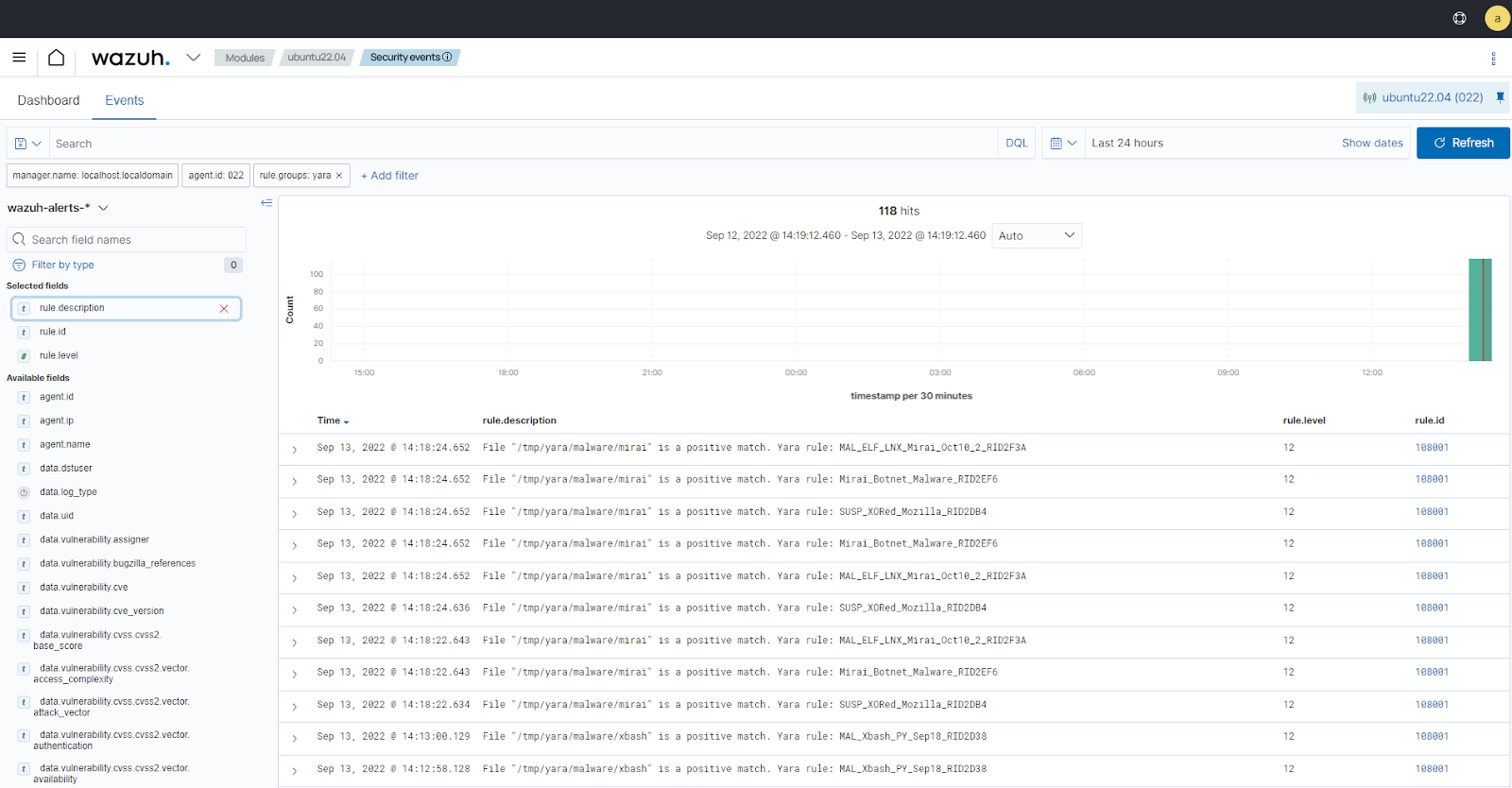
Configuration for Windows
Windows endpoint
Configure Python and YARA
Perform the following steps to install Python, YARA, and download YARA rules.
Download Python executable installer from the official Python website.
Run the Python installer once downloaded and make sure to check the following boxes:
Install launcher for all usersAdd Python 3.X to PATH. This places the interpreter in the execution path.
Download and install the latest Visual C++ Redistributable package.
Open PowerShell with administrator privileges to download and extract YARA:
> Invoke-WebRequest -Uri https://github.com/VirusTotal/yara/releases/download/v4.2.3/yara-4.2.3-2029-win64.zip -OutFile v4.2.3-2029-win64.zip > Expand-Archive v4.2.3-2029-win64.zip; Remove-Item v4.2.3-2029-win64.zip
Create a directory called
C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\bin\yara\and copy the YARA executable into it:> mkdir 'C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\bin\yara\' > cp .\v4.2.3-2029-win64\yara64.exe 'C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\bin\yara\'
Install the
valhallaAPImodule:> pip install valhallaAPI
Copy the following script and save it as
download_yara_rules.py:from valhallaAPI.valhalla import ValhallaAPI v = ValhallaAPI(api_key="1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111") response = v.get_rules_text() with open('yara_rules.yar', 'w') as fh: fh.write(response)
Run the following commands to download the rules and place them in the
C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\bin\yara\rules\directory:> python.exe download_yara_rules.py > mkdir 'C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\bin\yara\rules\' > cp yara_rules.yar 'C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\bin\yara\rules\'
Configure active response and FIM
Perform the steps below to configure the ThreatLockDown FIM and an active response script for the detection of malicious files on the endpoint.
Create the
yara.batscript in theC:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\bin\directory. This is necessary for the Wazuh-YARA active response scans:@echo off setlocal enableDelayedExpansion reg Query "HKLM\Hardware\Description\System\CentralProcessor\0" | find /i "x86" > NUL && SET OS=32BIT || SET OS=64BIT if %OS%==32BIT ( SET log_file_path="%programfiles%\ossec-agent\active-response\active-responses.log" ) if %OS%==64BIT ( SET log_file_path="%programfiles(x86)%\ossec-agent\active-response\active-responses.log" ) set input= for /f "delims=" %%a in ('PowerShell -command "$logInput = Read-Host; Write-Output $logInput"') do ( set input=%%a ) set json_file_path="C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\stdin.txt" set syscheck_file_path= echo %input% > %json_file_path% for /F "tokens=* USEBACKQ" %%F in (`Powershell -Nop -C "(Get-Content 'C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\stdin.txt'|ConvertFrom-Json).parameters.alert.syscheck.path"`) do ( set syscheck_file_path=%%F ) del /f %json_file_path% set yara_exe_path="C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\bin\yara\yara64.exe" set yara_rules_path="C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\bin\yara\rules\yara_rules.yar" echo %syscheck_file_path% >> %log_file_path% for /f "delims=" %%a in ('powershell -command "& \"%yara_exe_path%\" \"%yara_rules_path%\" \"%syscheck_file_path%\""') do ( echo wazuh-yara: INFO - Scan result: %%a >> %log_file_path% ) exit /b
Add the
C:\Users\<USER_NAME>\Downloadsdirectory for monitoring within the<syscheck>block in the ThreatLockDown agent configuration fileC:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\ossec.conf. Replace<USER_NAME>with the username of the endpoint:<directories realtime="yes">C:\Users\<USER_NAME>\Downloads</directories>
Restart the ThreatLockDown agent to apply the configuration changes:
> Restart-Service -Name wazuh
ThreatLockDown server
Perform the following steps on the ThreatLockDown server. This allows alerting for changes in the endpoint monitored directory and configuring an active response script to trigger whenever it detects a suspicious file.
Add the following decoders to the ThreatLockDown server
/var/ossec/etc/decoders/local_decoder.xmlfile. This allows extracting the information from YARA scan results:<decoder name="yara_decoder"> <prematch>wazuh-yara:</prematch> </decoder> <decoder name="yara_decoder1"> <parent>yara_decoder</parent> <regex>wazuh-yara: (\S+) - Scan result: (\S+) (\S+)</regex> <order>log_type, yara_rule, yara_scanned_file</order> </decoder>
Add the following rules to the ThreatLockDown server
/var/ossec/etc/rules/local_rules.xmlfile. The rules detect FIM events in the monitored directory. They also alert when malware is found by the YARA integration:<group name="syscheck,"> <rule id="100303" level="7"> <if_sid>550</if_sid> <field name="file">C:\\Users\\<USER_NAME>\\Downloads</field> <description>File modified in C:\Users\<USER_NAME>\Downloads directory.</description> </rule> <rule id="100304" level="7"> <if_sid>554</if_sid> <field name="file">C:\\Users\\<USER_NAME>\\Downloads</field> <description>File added to C:\Users\<USER_NAME>\Downloads directory.</description> </rule> </group> <group name="yara,"> <rule id="108000" level="0"> <decoded_as>yara_decoder</decoded_as> <description>Yara grouping rule</description> </rule> <rule id="108001" level="12"> <if_sid>108000</if_sid> <match>wazuh-yara: INFO - Scan result: </match> <description>File "$(yara_scanned_file)" is a positive match. Yara rule: $(yara_rule)</description> </rule> </group>
Add the following configuration to the ThreatLockDown server
/var/ossec/etc/ossec.conffile:<ossec_config> <command> <name>yara_windows</name> <executable>yara.bat</executable> <timeout_allowed>no</timeout_allowed> </command> <active-response> <command>yara_windows</command> <location>local</location> <rules_id>100303,100304</rules_id> </active-response> </ossec_config>
Restart the ThreatLockDown manager to apply the configuration changes:
$ sudo systemctl restart wazuh-manager
Attack emulation
Note
For testing purposes, we download the EICAR anti-malware test file as shown below. We recommend testing in a sandbox, not in a production environment.
Download a malware sample on the monitored Windows endpoint:
Turn off Microsoft Virus and threat protection.
Download the EICAR zip file:
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri https://secure.eicar.org/eicar_com.zip -OutFile eicar.zip
Unzip it:
> Expand-Archive .\eicar.zip
Copy the EICAR file to the monitored directory:
> cp .\eicar\eicar.com C:\Users\<USER_NAME>\Downloads
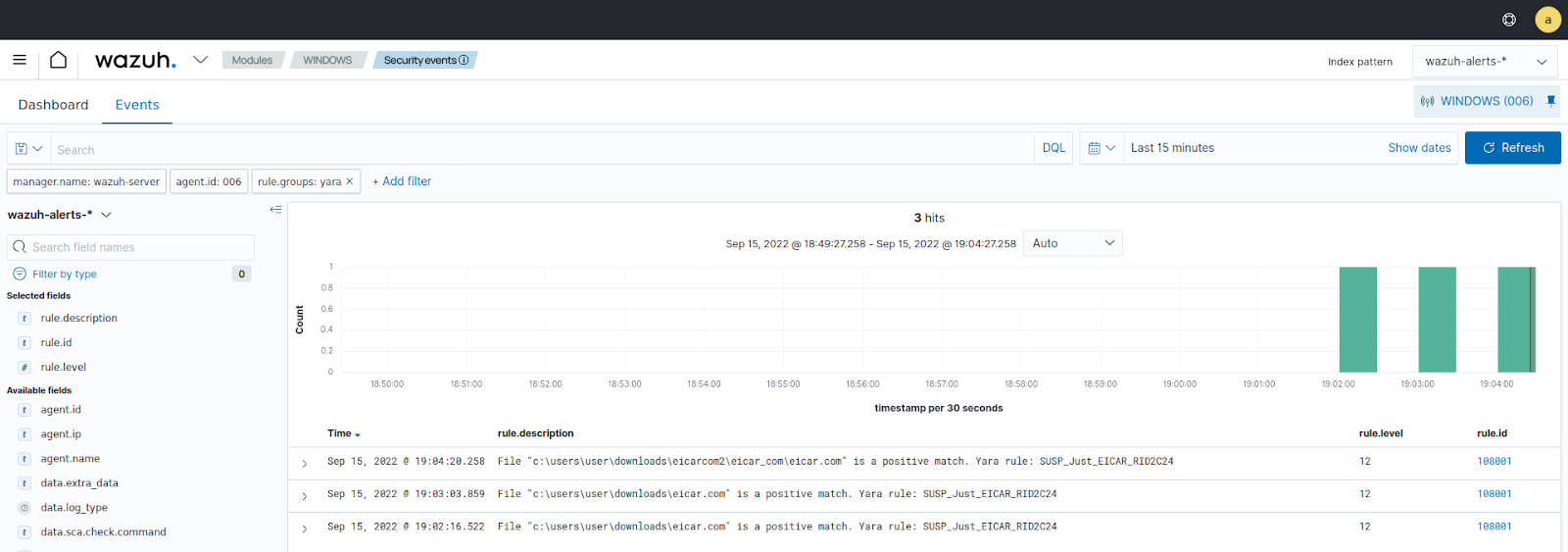
Visualize the alerts
You can visualize the alert data in the ThreatLockDown dashboard. To do this, go to the Threat Hunting module and add the filters in the search bar to query the alerts.
rule.groups:yara